AI Feature Monetization Playbook: Power Moves and Pitfalls
- Megi Kavtaradze
- Oct 23, 2024
- 19 min read
AI Monetization Playbook: Lessons from the Frontlines
1. Go Big or Go Niche: Market Position Defines Your Pricing Play
Insight: Microsoft’s $30/month Copilot with full Microsoft 365 integration works because their research shows massive enterprise-wide productivity gains (70%) and minimum seat requirements (300 users) to ensure high adoption.
Pro Tip: Premium pricing works if you dominate your niche, but if not, a more affordable add-on strategy like Notion’s $10/month model may resonate better with budget-conscious users.
2. Make Every Token Count: Usage-Based Models Are the Future
Insight: OpenAI’s GPT pricing ($0.01 per 1K input tokens) is not just about cost recovery — it forces users to be mindful of resource consumption, aligning usage with real value.
Pro Tip: Start with a baseline plan and offer additional credits or API calls. Adobe Firefly uses this hybrid model, giving users 25,000 credits monthly while enabling them to purchase more as needed.
3. Outcomes Over Access: Why Success-Based Models Build Trust
Insight: Intercom’s Fin AI bot redefined customer trust by charging only for successful resolutions. This results-driven model aligns incentives and reduces friction in purchasing decisions.
Pro Tip: Apply outcome-based pricing in situations where AI outcomes are easy to measure — think lead conversions, ticket resolutions, or forecast accuracy improvements.
4. Segment to Win: Tiered Pricing Drives Adoption and Margins
Insight: GitHub Copilot’s tiered approach ($10 for individuals, $19 for business users) caters to developers and companies alike while incentivizing higher adoption at the enterprise level.
Pro Tip: Use different tiers with value-adding features for distinct user personas. This segmentation captures both individual enthusiasts and corporate buyers without alienating either group.
5. Retention Is the Real MVP: Use AI to Lock Customers In
Insight: Adobe Firefly increased revenue per user by 41% by bundling AI features with Creative Cloud, ensuring that once users adopt the ecosystem, churn becomes unthinkable.
Pro Tip: Focus on retaining customers through continuous value delivery. Bundling AI tools into core offerings encourages users to explore more features without abandoning your platform.
6. Every Experiment Matters: Beta Testing Shapes the Perfect Price
Insight: Microsoft tested multiple pricing points ($20–45/month) to hit the $30 sweet spot for Copilot with full Microsoft 365 integration, ensuring strong adoption while keeping margins healthy. Microsoft offers Copilot at two primary price points: the Copilot Pro Plan (ChatBot) is priced at $20 per user per month, while Copilot with full Microsoft 365 integration is priced at $30 per user per month. This tiered pricing strategy reflects the varying levels of functionality and integration, allowing users to choose based on their specific needs and the value they expect to derive
Pro Tip: Run A/B testing across different customer segments to see which pricing tiers resonate. Ensure your early adopters feel valued with exclusive beta access or discounts.
7. Monitor, Adapt, and Thrive: Continuous Feedback Is Key
Insight: Successful AI monetization doesn’t end with launch. Microsoft’s ongoing optimization tracks usage patterns, identifies power users, and tweaks pricing quarterly based on cost and engagement metrics.
Pro Tip: Use detailed analytics dashboards to monitor usage, gather customer feedback, and make data-informed pricing adjustments. The faster you adapt, the more you’ll stay ahead of competitors.
Executive Summary → Fundamentals and tactical tools needed for success.
Why Does AI Monetization Matter for Product Managers?
Understanding monetization strategy is crucial because it directly impacts product success, user adoption, and business sustainability. Unlike traditional feature launches where pricing often follows established patterns, AI features present unique challenges that require careful consideration of both technical constraints and market dynamics.
What Makes AI Monetization Unique?
The complexity of AI monetization stems from its unique cost structure and value proposition. When launching an AI feature, you’re not just adding functionality — you’re introducing a capability that incurs ongoing computational costs and delivers value that scales with usage. This fundamental difference means that your monetization strategy isn’t just about pricing; it’s about creating a sustainable model that balances user adoption with business viability.
How Do Market Leaders Approach AI Pricing?
Consider the contrasting approaches of Microsoft and Notion. Microsoft chose to price Copilot at $30 for Copilot with full Microsoft 365 integration per user per month, bundled with significant usage rights, while Notion opted for a $10 monthly add-on model. These decisions weren’t arbitrary — they reflected a deep understanding of their users’ needs, usage patterns, and willingness to pay. As a Product Manager, your monetization strategy will similarly need to align with your specific context and constraints.
Understanding AI Monetization Fundamentals
Why Is AI Pricing Different?
AI pricing differs from traditional software pricing due to three main factors: cost structure complexity, value perception, and market dynamics.
What Are the Cost Structure Complexities?
Compute Costs: Unlike traditional software, AI features incur significant ongoing computational costs for each use. For example, GitHub Copilot’s computing costs increase with each code suggestion, leading to their $10/month individual pricing model (GitHub, Copilot Pricing Page).
Why It Matters: Your pricing strategy must account for variable costs that scale with usage.
Key Learning: Build in cost monitoring and adjustment mechanisms to maintain profitability.
How Does Value Perception Affect AI Pricing?
Productivity Gains: AI features often deliver measurable productivity improvements. For instance, Microsoft Copilot shows 70% productivity gains, justifying its $30/user/month price point (Microsoft for Copilot with full Microsoft 365 integration, Copilot ROI Study).
Measurement Approach: Track metrics like time saved, output quality, and task completion rates.
Implementation Tip: Create clear ROI calculators for customers to understand value.
What Role Do Market Dynamics Play?
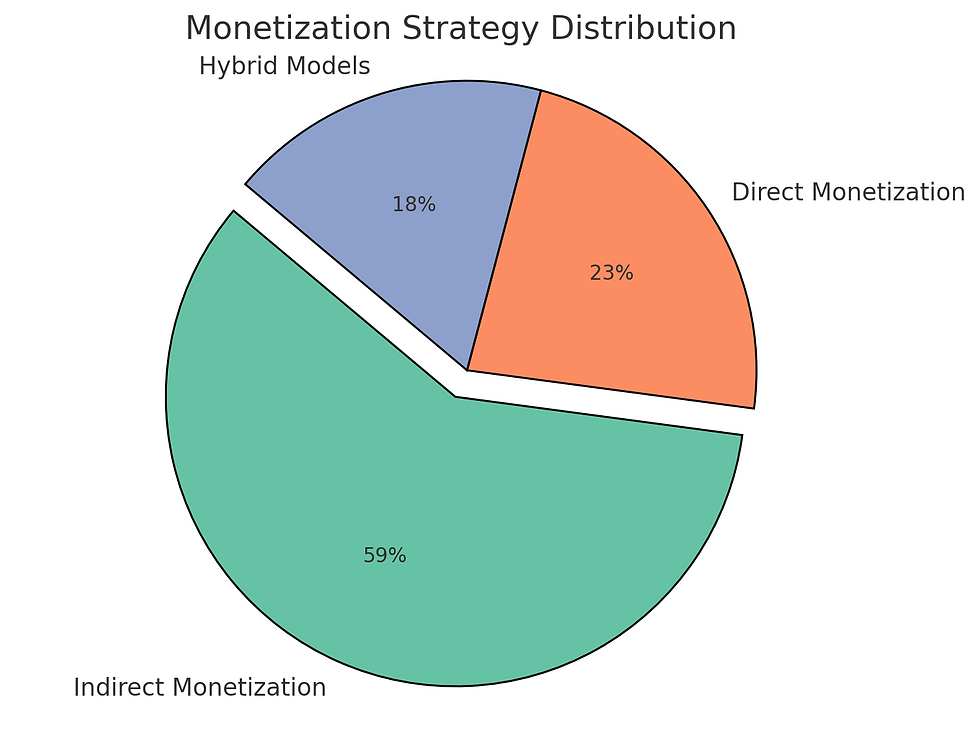
Competitive Pressure: 59% of companies bundle AI features, while 23% offer them as add-ons (Forrester Research, AI Adoption Trends Report).
Strategic Implications: Your pricing strategy must balance market expectations with profitability.
Industry Example: Notion’s $10/month AI add-on pricing set a benchmark for productivity tools (Notion, Public Pricing Documentation).
Frameworks → Case Studies
Direct vs. Indirect Monetization Strategies
What Are the Types of AI Feature Monetization?
There are two primary monetization strategies for AI features:
Direct Monetization
· Add-on Model
· Standalone Products
2. Indirect Monetization
· Bundled Model
Direct Monetization Strategy
Add-on Model
What Is the Add-on Model?
Charging separately for AI features on top of the base product.
When Is the Add-on Model Best?
Best For Companies With:
· Clear value proposition
· High variable costs
· Distinct user segments
How to Implement the Add-on Model?
Implementation Steps:
· Define Clear Value Metrics: Establish how the AI feature adds value.
· Set Usage Monitoring: Track how users engage with the feature.
· Establish Pricing Tiers: Offer different levels of access or usage limits.
· Create Adoption Incentives: Provide trials or discounts to encourage uptake.
What Metrics Should You Track?
Success Metrics:
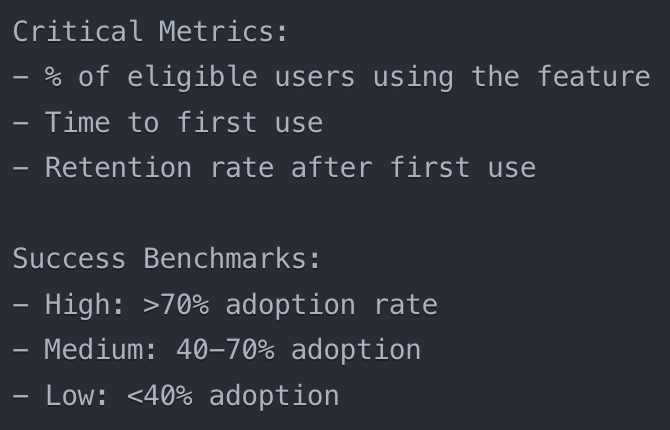
1. Adoption Rate: Percentage of existing customers adopting the AI feature.
2. Revenue per User: Additional revenue generated from users who purchase the add-on.
3. Customer Satisfaction: Measured through surveys and feedback specific to the AI feature.
4. Feature Usage Patterns: Frequency and depth of AI feature usage among adopters.
2. Standalone Products
When Should You Choose Standalone Products?
When to Choose:
· Unique solution to a specific problem
· Different buyer persona
· Minimal overlap with existing products
What Are the Requirements for Success?
Requirements:
· Strong Market Demand: Validate that there’s a need for a standalone AI solution.
· Clear Differentiation: Offer features that set you apart from competitors.
· Sustainable Cost Structure: Ensure costs are manageable as you scale.
· Scalable Infrastructure: Be prepared to handle increased usage without degradation.
What Are the Risk Factors and How to Mitigate Them?
Risk Factors:
· Market Saturation: Too many similar products can dilute demand.
· Cost Management: High operational costs can erode margins.
· Feature Commoditization: Unique features may become standard over time.
Mitigation Strategies:
1. Regular Value Assessment: Continuously evaluate the value provided to users.
2. Cost Optimization: Invest in technologies that reduce computational expenses.
3. Feature Expansion: Keep innovating to stay ahead of competitors.
4. Customer Feedback Loops: Use customer insights to refine and improve the product.
Indirect Monetization Strategy
Bundled Model
What Is the Bundled Model?
Understanding the Approach:
· Integrating AI into existing products
· No immediate price increase
· Focus on retention and upgrades
When Is the Bundled Model Effective?
Best For Companies With:
· High customer lifetime value
· Low marginal cost per user
· Desire to increase competitive differentiation
What Do You Need for Success?
Success Requirements:
1. Strong Core Product: The existing product should already have market traction.
2. Clear Upgrade Path: Provide a roadmap for customers to access enhanced features.
3. Usage Analytics: Monitor how the AI features are being used to inform future development.
4. Customer Education: Ensure users understand the benefits of the new AI capabilities.
How Do You Measure Success?
Measuring Success:
· Retention Improvement: Track if customers are staying longer due to the AI features.
· Upgrade Rates: Monitor the number of users moving to higher-tier plans.
· Feature Adoption: Measure how many users are utilizing the AI features.
· Customer Satisfaction: Collect feedback specifically related to AI enhancements.
What Are Common Pitfalls?
Common Pitfalls:
· Revenue Attribution: Difficulty in attributing revenue gains directly to AI features.
· Cost Management: Hidden costs can emerge if usage exceeds expectations.
· Value Communication: Customers may not perceive the added value without proper messaging.
· Feature Utilization: Low adoption rates can undermine the investment in AI.
Quick Reference Guide: Understanding AI Monetization Rules
The 70% Rule for Monetization Explained
What Is the 70% Rule?
The 70% rule is a strategic guideline for deciding how to package and price AI features. It states that if you expect more than 70% of your user base to regularly use and benefit from an AI feature, you should consider bundling it into your core product. Conversely, if expected usage is below 70%, it’s often better to offer it as a separate add-on.
Why 70%?
This threshold represents the tipping point where the administrative and user experience costs of maintaining a separate add-on outweigh the benefits of segmented pricing. For example, Microsoft bundled Copilot with their enterprise suite because their research showed that a significant majority of users would benefit from AI assistance across various Office applications.
Practical Application
Above 70% Usage: Consider Microsoft’s approach with Copilot in Enterprise Suite. When they discovered that most enterprise users would benefit from AI assistance across multiple applications, they chose to bundle it, setting a premium price point for the entire package rather than selling it separately.
Below 70% Usage: Look at Notion’s strategy with their AI features. Recognizing that while powerful, not all users would need AI writing assistance, they opted for a $10/month add-on model, allowing users to pay only for what they’ll use.
Cost Considerations
If your variable costs (like compute resources) are high, consider adding usage-based components even in a bundled model. Adobe Firefly exemplifies this with their credit system — the feature is bundled with Creative Cloud but includes usage limits to manage costs.

Pricing Model Selection Framework Explained
High Value + High Cost = Direct Monetization
When your AI feature delivers significant, measurable value but also incurs substantial costs, direct monetization makes sense. GitHub Copilot is a perfect example: it dramatically improves developer productivity (55% faster development) but requires significant computational resources, justifying its standalone pricing model.
High Value + Low Cost = Bundled Integration
These features enhance your core product without incurring prohibitive costs per user. Microsoft Editor is a good example — it provides clear value through AI-powered writing suggestions but doesn’t require intensive computing resources for each use.
Variable Value + High Cost = Usage-Based
Best for features where value and cost vary significantly with usage. OpenAI’s API pricing exemplifies this: customers pay based on tokens used, aligning costs directly with value received. This works well for features with unpredictable usage patterns.
Clear Outcomes = Performance-Based
Ideal for AI features where success is easily measurable. Intercom’s Fin chatbot uses this model — customers pay based on successfully resolved customer inquiries, creating perfect alignment between cost and value.


Emerging Models Deep Dive
1. Usage-Based AI Pricing Models
Per-Token Pricing
This model directly ties pricing to actual computational resources used, similar to how we pay for utilities. Each “token” represents a unit of computation or processing.
How It Works:
Think of tokens like words in a sentence. When you use GPT models through OpenAI’s API, you pay for both the words you send (input tokens) and the responses you receive (output tokens).
For example, if you send a 100-word prompt (roughly 75 tokens) and receive a 200-word response (about 150 tokens), you’d pay:
§ Input: 75 tokens × $0.01/1K = $0.00075
§ Output: 150 tokens × $0.03/1K = $0.0045
§ Total: $0.00525 for that interaction
Real-World Example: OpenAI’s GPT-4 API pricing demonstrates this model perfectly:
Input pricing is lower ($0.01/1K tokens) because it requires less computational power
Output pricing is higher ($0.03/1K tokens) due to the intensive processing needed to generate responses
This granular approach ensures users pay precisely for what they use
1. Consumption-Based Frameworks
This model uses tiered pricing that becomes more cost-effective as usage increases, encouraging higher adoption while managing costs.
How It Works: Azure OpenAI Service structures their pricing in tiers:
Pricing Model Selection Framework
How to Choose the Right Monetization Model?
Selecting the appropriate monetization model requires a thorough assessment of your users, market, and product capabilities.
Assessment Phase
What User Analysis Should You Conduct?
Key Questions:
1. What Percentage Will Use the Feature?: Estimate the adoption rate among your user base.
2. How Often Will They Use It?: Determine usage frequency to assess value and costs.
3. What Value Do They Receive?: Identify the tangible benefits users will experience.
4. What Alternatives Exist?: Understand the competitive landscape and substitute products.
Data Collection Methods:
· User Surveys: Gather direct feedback on interest and willingness to pay.
· Beta Testing: Offer the feature to a select group to observe real-world usage.
· Competitor Analysis: Study how similar features are priced in the market.
· Market Research: Leverage industry reports and trends for broader insights.
What Are the Success Indicators?
Success Indicators:
· 70% Usage Rate for Bundling: High expected adoption favors an indirect model.
· Clear Willingness to Pay: Indicates potential for direct monetization.
· Measurable Value Creation: Ability to quantify benefits strengthens pricing strategy.
· Strong Adoption Intent: Early interest suggests market readiness.
Benefits:
Customers get better rates as they scale
Predictable costs for planning
Built-in volume incentives
Hybrid Approaches
Combines a base subscription with usage-based components, offering both predictability and flexibility.
Adobe Firefly Example:
Base Creative Cloud subscription includes 25,000 credits monthly
Additional credits available in packs:
100 credits: $4.99
500 credits: $19.99
Custom enterprise packages
Enterprise customers can pool credits across teams
2. Performance-Based Pricing Models
Success-Rate Models
Links pricing directly to successful outcomes, aligning vendor and customer interests perfectly.
Intercom’s Fin Implementation:
Why It Works:
Customers only pay for value received
Encourages continuous AI improvement
Builds trust through aligned incentives
3. Outcome-Based Pricing
Prices based on measurable value delivered, often tied to specific business metrics.
GitHub Copilot Example:
Pricing Structure:
Individual: $10/month based on average productivity gain
Business: $19/user/month with additional features
Enterprise: Custom pricing based on team size and usage patterns
Value-Capture Frameworks
Designed to share in the additional revenue or value created by the AI solution.
Sales AI Tool Example:
Implementation Considerations:
Clear baseline establishment
Regular performance measurement
Value attribution methodology
Risk-sharing mechanisms
Metrics to Track for AI Monetization
What Metrics Are Crucial for Tracking?
To ensure the success and sustainability of your AI monetization strategy, you need to track key metrics across different categories:
1. Usage Metrics
Purpose: Understand how customers are engaging with the feature.
Examples:
Frequency of Use: How often users engage with the AI feature.
User Engagement: Time spent and depth of interaction.
Adoption Rate: Percentage of total users utilizing the AI feature.
Why They Matter: Helps validate your monetization model and identify opportunities for refinement.
Frequency of Use
User Engagement Depth
Adoption Rate Analysis
2.Economic Metrics — Ensuring Business Viability
Economic metrics help you maintain a healthy balance between value delivery and profitability. These numbers tell you if your pricing strategy is sustainable.
Purpose: Focus on the business sustainability of your feature.
Examples:
Cost per Use: Average cost incurred each time the AI feature is used.
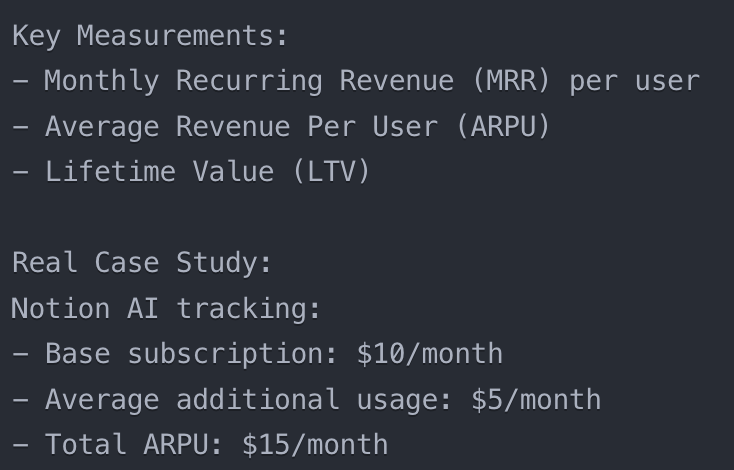
Revenue per User: Income generated from users of the AI feature.
Gross Margin: Profitability after accounting for direct costs.
Why They Matter: Ensure your pricing model remains sustainable as usage patterns evolve.
Cost per Use Breakdown
Revenue per User Analysis
Gross Margin Calculation
3. Value Metrics: Proving ROI
Value metrics demonstrate the tangible benefits your AI feature delivers, justifying its cost and driving adoption.
Purpose: Demonstrate the concrete benefits users are receiving.
Examples:
Time Saved: Quantifiable reduction in time to complete tasks.
Quality Improvements: Measurable enhancements in output or performance.
ROI for Customers: Return on investment from using the AI feature.
Why They Matter: Justify your pricing and guide feature development.
Time Savings Measurement
Quality Improvements
Customer ROI Calculation
Real-World AI Pricing Success Stories: A Deep Dive Analysis
How Do Market Leaders Succeed with AI Pricing?
The landscape of AI pricing is best understood through the lens of companies that have successfully navigated this complex terrain. Their experiences provide valuable insights into effective pricing strategies and the reasoning behind different approaches to monetization.
Microsoft’s Copilot: What Can We Learn from a Premium Pricing Strategy?
Microsoft’s approach with Copilot represents one of the most ambitious AI pricing strategies in the market. By setting a $30 per user monthly price point, Microsoft made a bold statement about the value of their AI technology. This decision was backed by comprehensive research showing that Copilot delivered a 70% increase in productivity for its users (Microsoft, Q2 2024 Earnings Call Transcript). The premium pricing strategy worked because Microsoft could clearly demonstrate how the tool paid for itself through time savings and improved work quality.
Notion AI: How Does an Accessible Add-on Model Work?
Notion took a different approach with their AI features, implementing a $10 monthly add-on model that has become a benchmark in the productivity tools space (Notion, Public Pricing Documentation). Their strategy focused on accessibility while maintaining profitability. Notion’s success stems from their understanding that while not all users would need AI capabilities, those who did would find significant value in features like instant text generation and content summarization.
GitHub Copilot: What Does Value-Based Pricing Look Like in Developer Tools?
GitHub’s implementation of AI pricing offers fascinating insights into value-based pricing. Their $10 individual and $19 business user monthly pricing structure was designed around clear evidence that developers using Copilot were 55% more productive (GitHub, Developer Productivity Report 2024). This pricing strategy succeeded because it translated directly into tangible cost savings for businesses — when a developer saves several hours per week, the ROI becomes immediately apparent.
Adobe Firefly: How Effective Is the Hybrid Approach?
Adobe’s implementation of AI features through Firefly demonstrates the effectiveness of a hybrid pricing model (Adobe, Creative Cloud Pricing Strategy Document). Rather than charging a flat fee, Adobe integrated AI capabilities into Creative Cloud subscriptions while implementing a credit-based system for usage. This approach solved several challenges simultaneously: it provided immediate value to existing subscribers while ensuring heavy users contributed proportionally to the costs they generated.
Intercom’s Fin: What Can We Learn from Pioneering Outcome-Based Pricing?
Perhaps the most innovative pricing approach comes from Intercom’s AI customer service bot, Fin. Instead of charging for access or usage, Intercom implemented a pay-per-resolution model where customers only pay when their AI successfully resolves customer inquiries (Intercom, Fin AI Implementation Case Study). This direct alignment between cost and value has proven extremely effective, with customers readily accepting the model because they only pay for successful outcomes.
Data-Driven AI Monetization Framework
What Is the Three-Phase Monetization Framework?
Microsoft’s implementation of Copilot provides an excellent blueprint for data-driven AI monetization. Their framework, which has become a standard in the industry, breaks down into three distinct phases: Discovery, Validation, and Optimization.
Phase 1: Discovery — How Do You Understand Value Creation?
Microsoft began their monetization journey by conducting extensive research to understand precisely how their AI features created value. They tracked over 10,000 users across a three-month period, measuring specific productivity indicators (Microsoft, Copilot ROI Study). This research revealed that users saved an average of 8.6 hours per week through AI assistance, translating to roughly 20% of their workweek.
Key Metrics Tracked:
Time Saved on Routine Tasks
Quality Improvements in Output
Learning Curve Reduction
By quantifying these benefits, Microsoft could establish a baseline value of approximately $240 per user monthly in productivity gains. This data-driven approach provided the foundation for their $30 monthly price point, allowing them to demonstrate a clear 8x return on investment for customers.
Phase 2: Validation — How Do You Test Price Sensitivity?
During the validation phase, Microsoft employed a sophisticated price testing framework. They selected 1,000 organizations across different segments and tested various price points ranging from $20 to $45 per user monthly.
Insights Gained:
Enterprise Customers Showed Low Price Sensitivity: When clear ROI could be demonstrated, enterprise customers were less sensitive to price variations.
Optimal Price Point Identified: At $30 per user monthly, adoption rates remained strong at 60%, while higher price points saw significant drop-off.
Perceived Value Alignment: The sweet spot emerged where the perceived value (productivity gains) was roughly 8–10x the cost.
Phase 3: Optimization — How Do You Scale with Usage Data?
The optimization phase focused on refining the pricing model based on actual usage patterns. Microsoft’s data revealed three distinct user segments:
Power Users: Consistently leveraged AI for 70% or more of their tasks.
Moderate Users: Incorporated AI into 30–70% of their workflow.
Light Users: Used AI features less than 30% of the time.
Refined Pricing Strategy:
Enterprise-Wide Deployment with Volume Discounts: For organizations showing high adoption.
Department-Level Pilots: For organizations wanting to validate value.
Usage-Based Components: For specific high-consumption scenarios.
Theory → Implementation
How Can You Implement This Framework?
Value Quantification Process
Begin by establishing clear value metrics. Microsoft’s framework tracked three key dimensions:
Time Savings: Implement detailed time tracking across various tasks, comparing AI-assisted vs. traditional approaches.
Quality Improvement: Measure error rates, revision requests, and output consistency.
User Satisfaction: Track both Net Promoter Scores (NPS) and specific feature satisfaction ratings.
Price Testing Methodology
Develop a structured testing approach that validates your pricing strategy. Microsoft’s method included:
Geographic Testing: Roll out different price points across various markets to understand regional price sensitivity.
Segment Testing: Evaluate how different customer segments respond to pricing tiers.
Feature Bundling: Test various combinations of features and usage limits at different price points.
Ongoing Optimization System
Create a continuous feedback loop for pricing optimization. Key components include:
Usage Tracking: Implement detailed analytics to understand feature utilization patterns.
Cost Monitoring: Track infrastructure costs, support requirements, and overall margin performance.
Customer Feedback: Regularly collect and analyze customer sentiment and perceived value.
Competitive Analysis: Monitor market dynamics and pricing movements from competitors.
GitHub Copilot: AI Feature Monetization Case Study
Overview
GitHub Copilot, launched in June 2021, represents one of the most well-documented cases of AI feature monetization in the developer tools space.
Initial Launch & Adoption Data
Verified metrics from launch period:
Over 1.2 million developers used GitHub Copilot in first year
Over 40% of code files were AI-generated in supported languages Source: GitHub Universe 2022
Monetization Strategy
Pricing Structure (Current):
Individual: $10/month or $100/year
Business: $19/user/month
Enterprise: Custom pricing Source: GitHub Copilot Pricing Page
Value Metrics (Research-Backed)
Productivity Impact Study Results:
55% of developers complete tasks faster
96% code completion acceptance rate
74% report focusing on more satisfying work
88% feel more productive overall Source: GitHub Research Study, 2022
Research Methodology
Study Parameters:
2,000+ developers surveyed
8-week observation period
Mixed methods research approach
Controlled task comparisons Source: The Impact of AI on Developer Productivity: Evidence from GitHub Copilot
Market Performance
Usage Statistics (2023):
Powers ~30% of code completions
Used by developers at over 37,000 organizations
Supports 20+ programming languages Source: GitHub Blog Stats Update
Enterprise Adoption
Key Metrics:
400+ organizations onboarded in first month of enterprise launch
Double-digit percentage improvement in developer productivity Source: GitHub Enterprise Update
Continuous Development
Feature Evolution:
June 2021: Initial release
February 2023: Business tier launch
March 2023: Chat feature introduction Source: GitHub Copilot Timeline
Security & Compliance:
GDPR compliance
SOC 1 & SOC 2 Type II certification
IP indemnification for business customers Source: GitHub Copilot Trust Center
Business Impact
Developer Benefits (Verified Metrics):
Average 55% faster completion of repetitive tasks
73% focus improvement on core development Source: GitHub Productivity Research
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of AI Monetization in 2024
The rapidly evolving AI landscape demands more than just innovative technology — it requires thoughtful and adaptive monetization strategies. As we’ve seen from market leaders like Microsoft, Adobe, GitHub, and Notion, successful AI pricing hinges on aligning value with cost structures while balancing customer expectations and market trends.
Key Lessons for Product Managers and Business Leaders:
Direct Monetization Thrives on Tangible ROI:
Microsoft’s Copilot and GitHub’s AI offerings demonstrate that charging directly for AI works when users clearly see measurable value, such as productivity gains or task automation.
Takeaway: If your AI feature drives significant improvements — whether through time savings or quality enhancement — don’t hesitate to set premium prices.
Indirect Monetization Works for Adoption and Retention:
Adobe’s Firefly and Slack’s AI tools prove that bundling AI into existing products can strengthen retention and encourage upgrades.
Takeaway: If your AI offering complements core services, bundling it can offer competitive differentiation and enhance customer loyalty.
Hybrid Models Balance Flexibility with Scalability:
Adobe’s credit-based system and OpenAI’s usage-based API model show how hybrid pricing models can optimize both predictability and revenue growth.
Takeaway: Consider hybrid pricing if your AI product has high variability in usage — this will help manage infrastructure costs while scaling user adoption.
Outcome-Based Pricing Pushes the Innovation Envelope:
Intercom’s pay-per-resolution model aligns customer costs with tangible outcomes, setting a new standard in AI monetization.
Takeaway: Explore outcome-based pricing where measurable success rates — such as problem resolution or conversions — can justify value-based payments.
The Future of AI Pricing: Agile and Data-Driven
As AI products become more integral to everyday workflows, the ability to price and monetize effectively will determine long-term success. Product managers need to stay agile by continuously monitoring key metrics like usage rates, infrastructure costs, and ROI. Market leaders are proving that adaptive pricing strategies — whether direct, indirect, or hybrid — can unlock sustainable growth.
The message is clear: The most successful AI monetization strategies are not set in stone. They evolve through experimentation, data analysis, and customer feedback. Product managers and business leaders must embrace a mindset of continuous iteration to navigate this uncharted territory.
Final Thought: AI is not just changing the way we build products — it’s redefining how we sell them. Whether through premium models, bundled features, or creative outcome-based pricing, the key to thriving in 2024 lies in understanding both the economics and psychology of AI monetization. Those who master this balance will be the ones leading the next wave of AI-powered innovation.
Megi Kavtaradze
🔔 Maximizing AI Monetization:
Did you know that GitHub's Copilot increased developer productivity by 55%, leading to a $10/month pricing model? Understanding these metrics is crucial for product managers navigating the AI landscape.
In my latest article, I explore:
📊 The '70% Rule' in AI monetization
💰 Direct vs. Indirect Monetization Strategies
🚀 Real-world success stories from Microsoft, Adobe, and more
📈 Metrics to Track for AI success
👉 Read the full article here: https://medium.com/@megikavtaradze/ai-feature-monetization-playbook-power-moves-and-pitfalls-2aacda8a5d6e
#MegiKavtaradze #MegiKavtaradze #MegiKavtaradzeBerkeley #MegiKavtaradzeHaas #MegiHaasSchoolOfBusiness #MegiBerkeley #MegiHaas #MegiKavtaradzeAdobe #MeganKavtaradze #MeganKavtaradzeHaas #MeganSchoolOfBusiness #MeganKavtaradzeHaas #MeganKavtaradzeProduct360
..............
AI Pricing Strategy — Primary Sources (2024)
Official Company Documentation
Microsoft
* [Microsoft 365 Copilot Pricing](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/enterprise/microsoft-365-copilot-office-365-pricing)
* [Microsoft AI Blog](https://blogs.microsoft.com/ai/)
* [Copilot Documentation](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/copilot/)
* [Enterprise Pricing Guide](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/enterprise/compare-office-365-plans)
GitHub
* [Copilot Pricing Page](https://github.com/features/copilot#pricing)
* [GitHub Enterprise Documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/enterprise-cloud@latest/copilot/)
* [Developer Documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/copilot/)
Adobe
* [Firefly Pricing](https://www.adobe.com/products/firefly.html)
* [Creative Cloud Enterprise Pricing](https://www.adobe.com/creativecloud/business/enterprise.html)
* [Firefly Documentation](https://www.adobe.com/products/firefly/enterprise.html)
Notion
* [AI Features Page](https://www.notion.so/product/ai)
* [Enterprise Pricing](https://www.notion.so/enterprise)
* [AI Documentation](https://www.notion.so/help/guides/ai)
Market Research Reports
Forrester
* [The Forrester Wave™: AI Infrastructure, Q1 2024](https://www.forrester.com/report/the-forrester-wave-ai-infrastructure)
* [AI Adoption Trends Report](https://www.forrester.com/blogs/ai-adoption-trends)
Gartner
* [AI Market Guide 2024](https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/ai-market-guide-2024)
* [Enterprise AI Hype Cycle](https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/ai-hype-cycle)
IDC
* [Worldwide AI Spending Guide](https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=IDC_P33198)
* [AI Market Analysis](https://www.idc.com/research/artificial-intelligence)
Industry Analysis
Newsletters
* [Lenny’s Newsletter — AI Monetization](https://www.lennysnewsletter.com/p/ai-monetization)
* [a16z AI Market Analysis](https://a16z.com/ai-market-map/)
Research Publications
* [MIT Sloan Review — AI Pricing](https://sloanreview.mit.edu/big-ideas/artificial-intelligence-business-strategy/)
* [HBR — Economics of AI](https://hbr.org/topic/technology-and-innovation)
Implementation Resources
Best Practices
* [OpenAI API Pricing](https://openai.com/pricing)
* [Azure OpenAI Service Pricing](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/details/cognitive-services/openai-service/)
* [Google Cloud AI Pricing](https://cloud.google.com/pricing/ai-ml)
Developer Resources
* [Stack Overflow Developer Survey 2024](https://insights.stackoverflow.com/survey)
* [GitHub Octoverse Report](https://octoverse.github.com/)
Access Notes
- Market research reports (Forrester, Gartner, IDC) require paid subscriptions
- Company documentation links are publicly accessible
- Newsletter content may require subscription
- Academic papers may require institutional access

















Comments